Cubic Spline 三次样条曲线
System Model
For a group of certain points \((x_{0,1},x_{0,2},\cdots,x_{0,m}),(x_{1,1},x_{1,2},\cdots,x_{1,m}), (x_{2,1},x_{2,2},\cdots,x_{2,m}), \cdots, (x_{n,1},x_{n,2},\cdots,x_{n,m})\), we want to find a smooth enough curve that passes all these points to achieve the interpolation goal. To do so, we can use piecewise cubic functions to fitting the points.
Let's talk about a specific dimention \(k\) first. To simplify the denotation, we let \(x_i=x_{i,k}\). For a set of \(n+1\) points \((x_{0,k},x_{1,k},x_{2,k},\cdots,x_{n,k})\) and for the \(i\)-th piece of the spline, we can represent it by
To ensure the smooth of the curve, we write down the constraints,
Apply \(a_i,b_i,c_i,d_i\) to the constraints, we get
So we can get the following expressions
Open Loop
Assume stationary boundary \(S_0'(0)=0,S_{n-1}'(1)=0\), which is \(c_0=0, 3a_{n-1}+2b_{n-1}+c_{n-1}=0\).
You can suppose \(x_{n+2}=x_{n+1}\), so that \(x_{n+2}-2x_{n+1}+x_n=-x_{n+1}+x_n\)
Convert the expressions into matrix form, we have
Closed Loop
If the curve is a closed loop, \(x_0=x_{n+1}\). Then \(S_0'(0)=S_{n-1}'(1), S_0''(0)=S_{n-1}''(1)\), which means \(c_0=3a_{n-1}+2b_{n-1}+c_{n-1}\) and \(3a_{n-1}+b_{n-1}=b_0\).
Demo Code
2D Case
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 2D case
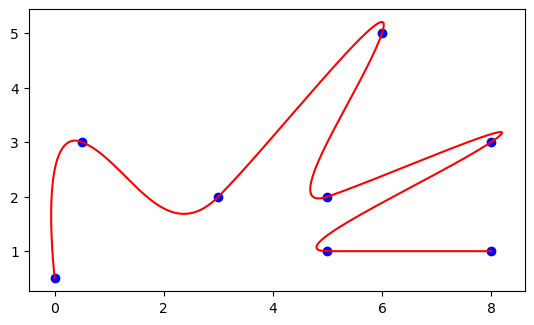
x = np.array([[0,0.5],[0.5,3],[3,2],[6,5],[5,2],[8,3],[5,1],[8,1]])
n = len(x) - 1
m = len(x[0])
# form t matrix
t1 = np.reshape(np.linspace(0, 1, 1001), [1, 1001])
t2 = t1 ** 2
t3 = t1 ** 3
t0 = np.reshape([1 for _ in range(1001)], [1, 1001])
# calculate A
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
tmp[0, 0] = 2
tmp[0, 1] = -3
tmp[0, 2] = 1
for i in range(1,n-1):
tmp[i, i] = 1
tmp[i, i+1] = -2
tmp[i, i+2] = 1
tmp[-1, -1] = -1
tmp[-1, -2] = 1
A = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate B
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
tmp[0, 0] = -3
tmp[0, 1] = 4
tmp[0, 2]= -1
for i in range(1,n-1):
tmp[i, i] = -1
tmp[i, i+1] = 2
tmp[i, i+2] = -1
tmp[-1, -1] = 1
tmp[-1, -2] = -1
B = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate C
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
for i in range(1, n):
tmp[i, i] = -1
tmp[i, i+1] = 1
C = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate D
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
for i in range(0, n):
tmp[i, i] = 1
D = tmp.dot(x)
# combine cubic splines together
y = np.array([])
for i in range(n):
if len(y) == 0:
y = np.reshape(A[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t3) + \
np.reshape(B[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t2) + \
np.reshape(C[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t1) + \
np.reshape(D[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t0)
else:
y = np.append(y, (
np.reshape(A[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t3) + \
np.reshape(B[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t2) + \
np.reshape(C[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t1) + \
np.reshape(D[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t0)
), axis=1)
# 2D plot
plt.plot(y[0], y[1], color='red')
plt.scatter(x.T[0], x.T[1], color='blue')
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
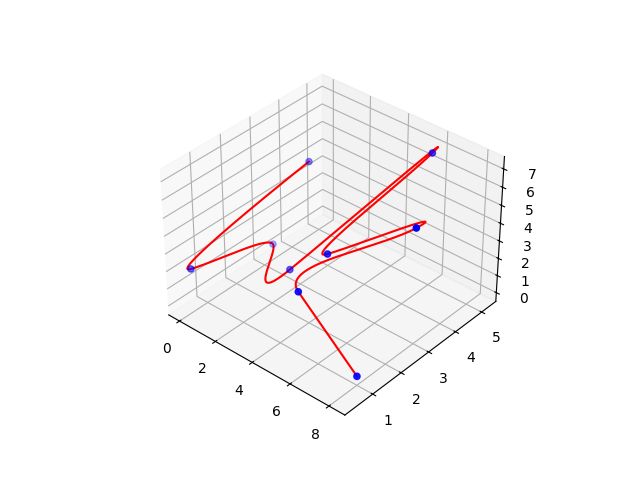
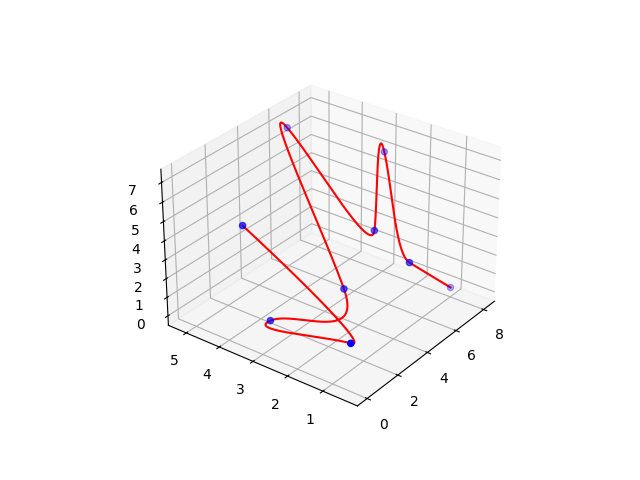
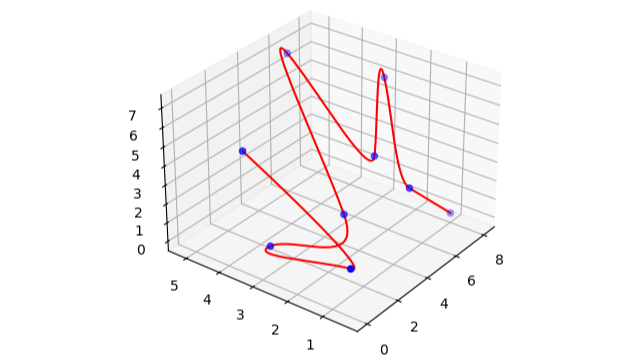
3D Case
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 3D case
x = np.array([[1,4,5],[0,0.5,2],[0.5,3,1],[3,2,2],[6,5,7],[5,2,4],[8,3,6],[5,1,3],[8,1,0]])
n = len(x) - 1
m = len(x[0])
# form t matrix
t1 = np.reshape(np.linspace(0, 1, 1001), [1, 1001])
t2 = t1 ** 2
t3 = t1 ** 3
t0 = np.reshape([1 for _ in range(1001)], [1, 1001])
# calculate A
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
tmp[0, 0] = 2
tmp[0, 1] = -3
tmp[0, 2] = 1
for i in range(1,n-1):
tmp[i, i] = 1
tmp[i, i+1] = -2
tmp[i, i+2] = 1
tmp[-1, -1] = -1
tmp[-1, -2] = 1
A = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate B
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
tmp[0, 0] = -3
tmp[0, 1] = 4
tmp[0, 2]= -1
for i in range(1,n-1):
tmp[i, i] = -1
tmp[i, i+1] = 2
tmp[i, i+2] = -1
tmp[-1, -1] = 1
tmp[-1, -2] = -1
B = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate C
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
for i in range(1, n):
tmp[i, i] = -1
tmp[i, i+1] = 1
C = tmp.dot(x)
# calculate D
tmp = np.zeros((n, n + 1))
for i in range(0, n):
tmp[i, i] = 1
D = tmp.dot(x)
# combine cubic splines together
y = np.array([])
for i in range(n):
if len(y) == 0:
y = np.reshape(A[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t3) + \
np.reshape(B[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t2) + \
np.reshape(C[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t1) + \
np.reshape(D[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t0)
else:
y = np.append(y, (
np.reshape(A[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t3) + \
np.reshape(B[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t2) + \
np.reshape(C[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t1) + \
np.reshape(D[i], [-1, 1]).dot(t0)
), axis=1)
# 3D plot
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.scatter3D(x.T[0], x.T[1], x.T[2], color='blue')
ax.plot3D(y[0], y[1], y[2], color='red')
plt.show()